Optogenetics Solutions
Flexible system for YOUR experimental needs.

All-in-one solutions
- Light Sources
- Combine with behavior
- Rotary Joints for Freely-moving animals
- Simple synchronization
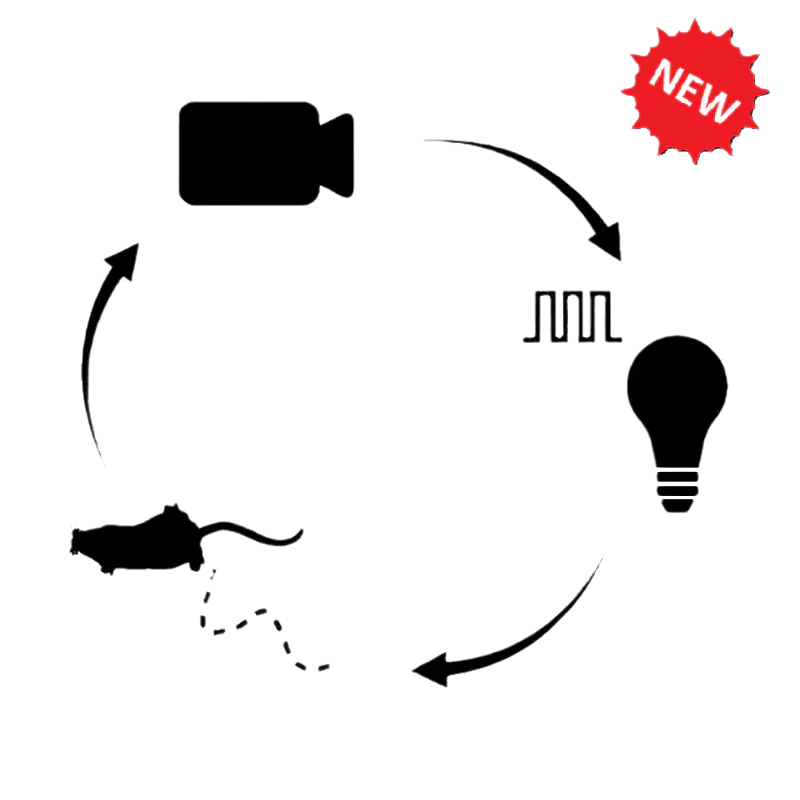
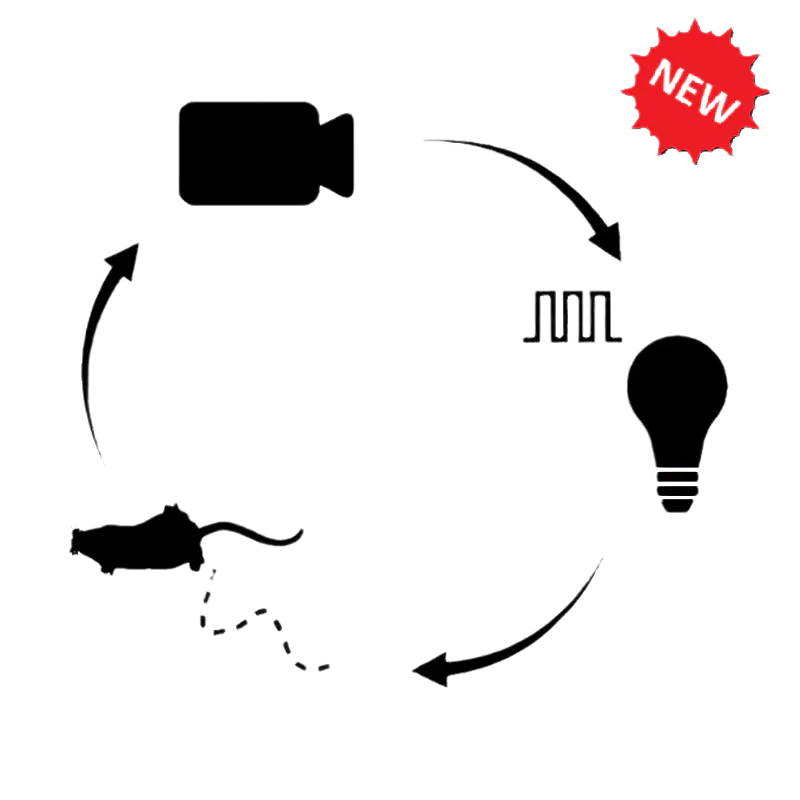
- Close-loop optogenetics
Multi-colors
Multi-sites / animals
Freely-moving
Customizable
Optogenetics is a groundbreaking technique that provides real-time, optical control of neuronal activity. Throughout the years, it has played a vital role in dissecting brain circuitry, probing the neural basis of behavior, modeling neurological disorders, and developing next-generation therapies in neuroscience and psychiatry.
The process requires expressing opsins, light-sensitive ion channels or pumps, in a specific neuronal population. For chronic experiments, a fiber-optic cannula is then surgically implanted above the target region to deliver a specific wavelength of light, activating or inhibiting the opsin-expressing cells. For example, blue light activates opsins like Channelrhodopsin (ChR2), while yellow or red light targets opsins such as NpHR or Jaws. For a list of available opsins, see the OPSIN APPLICATION NOTE.
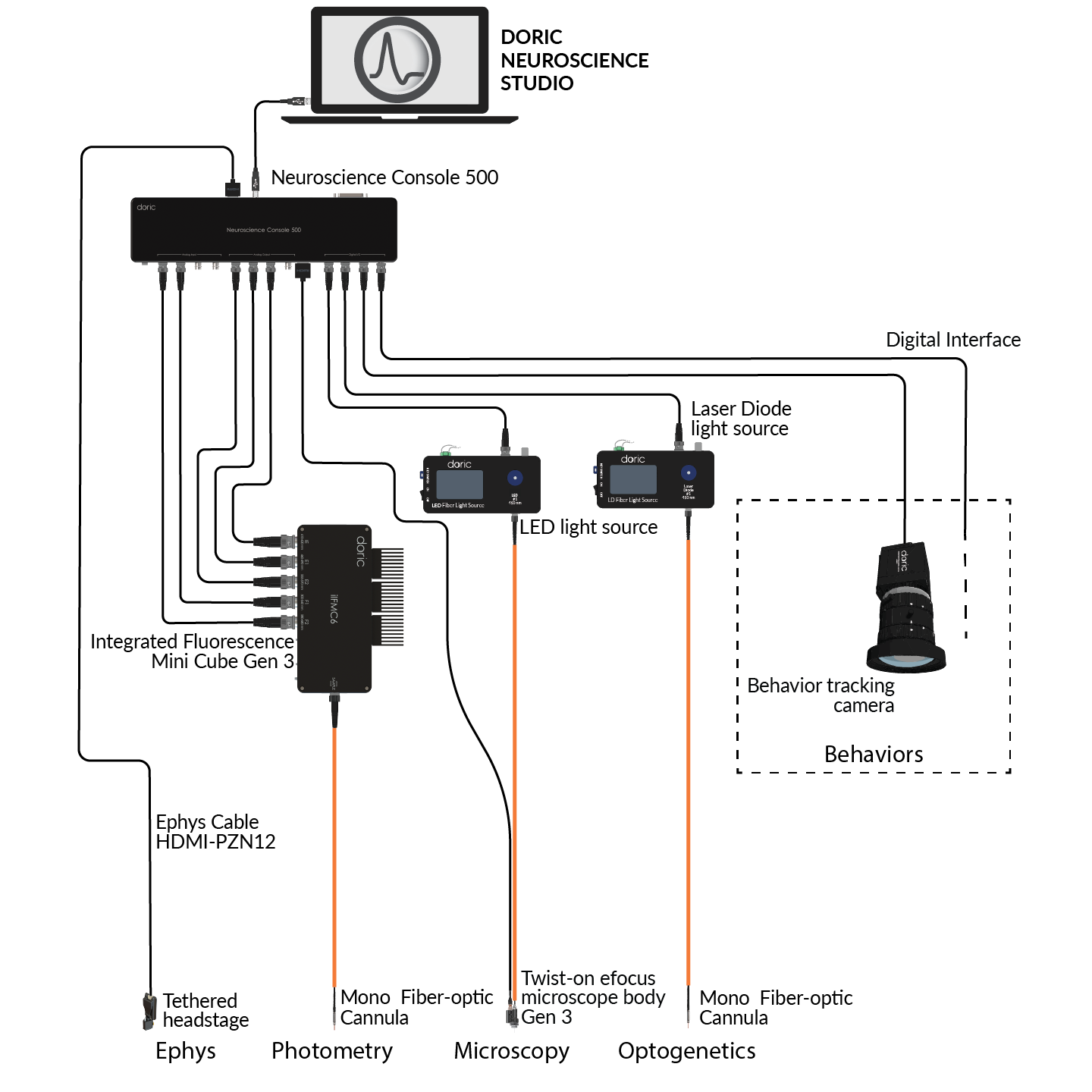
There is multiple experimental conditions that requires different components to bring the optogenetics light to the biological sample. It goes from acute experiment where the sample is fixed and you need very localized control of light spatial and temporal pattern, to complex experiment of involving freely moving animals where larger volume of neurons should be illuminated. In order to help selecting the right hardware components, we describe below the principal parts of the optogenetics systems with suggestion of best components to consider for a given context.
Choosing the right light source is one of the most important steps when designing an optogenetics experiment. The optimal light sources depend on opsin requirements (excitation wavelength & intensity), the size of the region(s)-of-interest and whether the animal is freely- moving.

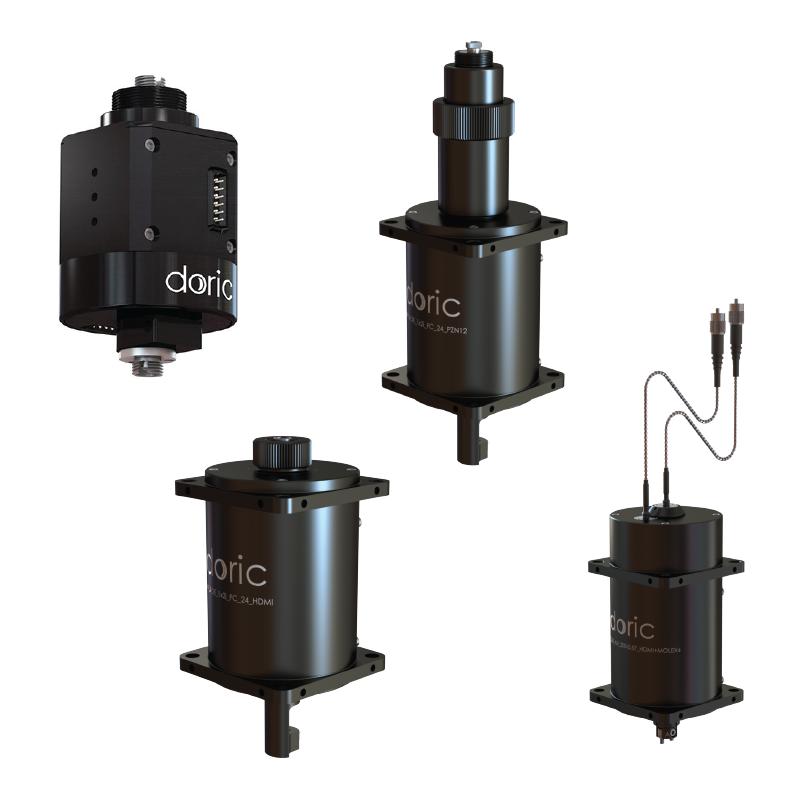
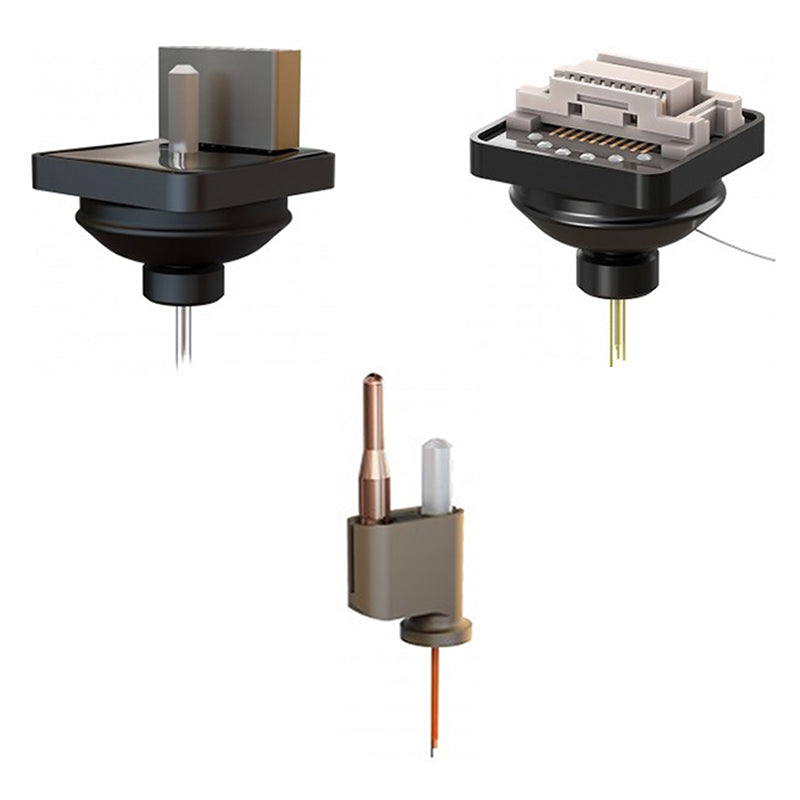
When performing optogenetic stimulation in freely-moving animals using a tethered setup, it is important to minimize cable tangling for unrestricted movement. To achieve this, a rotary joint (commutator) is often required. Rotary joints come in various depending on the experimental application. In general, consider the following three points when selecting the appropriate rotary joint:
- Optogenetics Only: If optogenetic stimulation is the sole optical requirement in your experiment, a non-pigtailed rotary joint is sufficient.
- Optogenetics + Fiber Photometry: If the rotary joint is intended for both optogenetics and fiber photometry, a pigtailed rotary joint is necessary.
- Optogenetics + Electrophysiology: To combine optogenetics with electrophysiology (e.g., EEG, Neuropixels), an opto-electric pigtailed rotary joint is required.
- For one optical stimulation site → Use a 1×1 rotary joint
- For two optical independent sites → Use a 2×2 rotary joint
- To split light from one source into two sites (optogenetics only) → Use a 1×2 rotary joint
Some neuroscience experiments, such as bilateral, multi-site and/or multi-animal optogenetics, require splitting the light from a single light source into multiple fibers. To effectively split light for these applications, several solutions are available. The optimal splitter type depends on the light source (LED, LISER or laser diode), the intensity requirements and the size of the region-of-interest.
Certain experiments require delivering multiple wavelengths of light to the same target brain region for various applications. For instance, to manipulate different neural populations expressing different opsins (ChR2 & ChrimonR), for bidirectional control of the same population (excitation/inhibition). Some special opsins are engineered to respond to mutliple wavelengths, such as step-function opsins, or can be toggled on/off with distinct wavelengths.
Doric Lenses offers several reliable and customizable light-combining solutions:
Maintaining optogenetics light power within the appropriate range is essential to prevent issues such as photobleaching, tissue overheating, and other unwanted side effects. However, under certain conditions, the light output from the source may exceed the optimal level for optogenetic applications—even when operating close to the threshold current setting. It is also not recommended to drive a light source close to the threshold for stability issues. In such cases, an additional component is required to deliberately reduce the light intensity.
Doric Lenses offers different customizable light-attenuating solutions:
Notes:
- For attenuating patch cords, optical transmission is specified for visible light and measured at a wavelength of 465 nm. At shorter wavelengths—such as 405 nm (UV)—the transmission is typically about half the specified value.
- Attenuating filters can also be integrated into branching fiber-optic patch cords upon request.
Combine your system with...
Optogenetics is commonly combined with complementary neuroscience techniques such as behavior measurements, fiber photometry, Doric miniscopes, fluidic injections, and electrophysiology to gain a deeper understanding of neural circuit function in vivo.
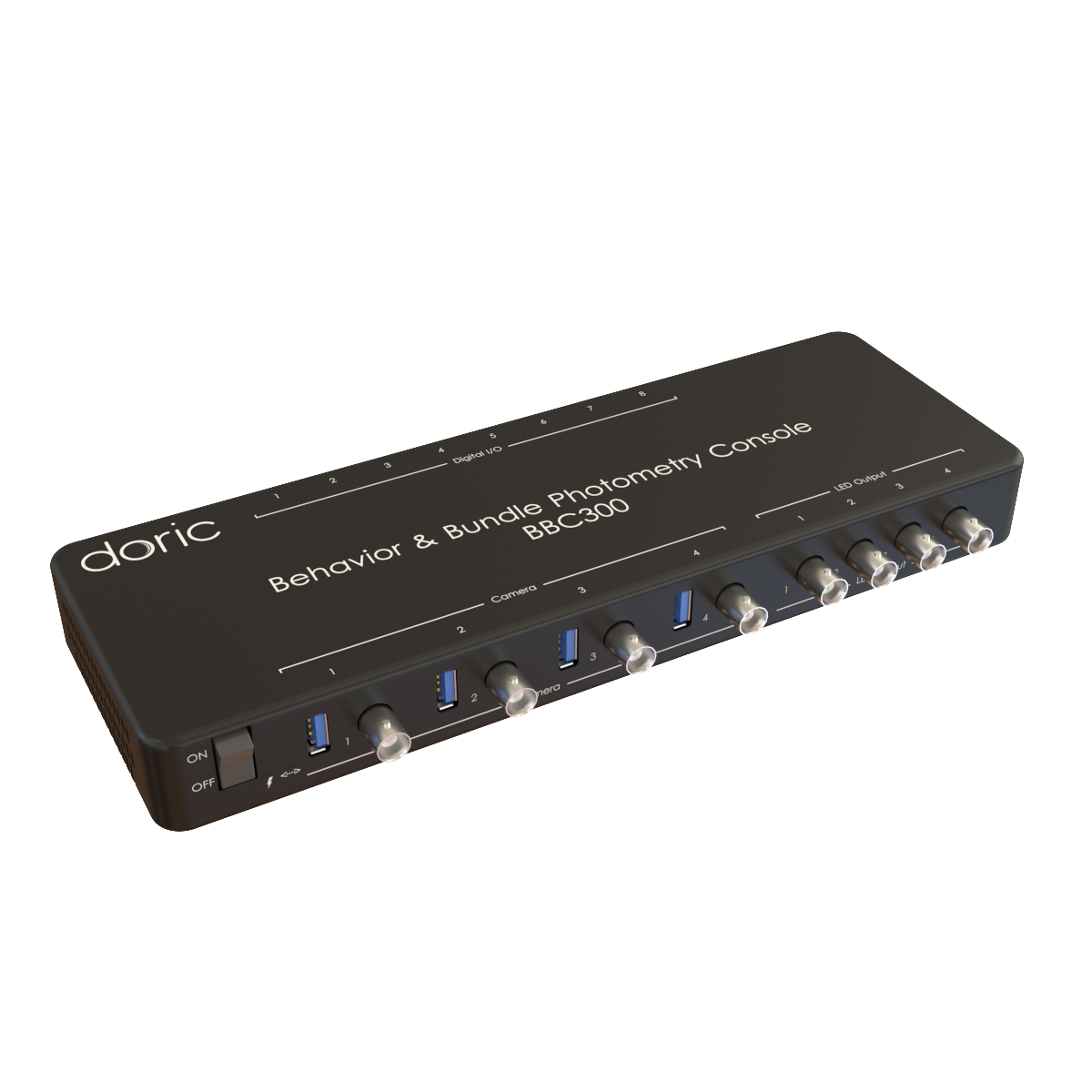
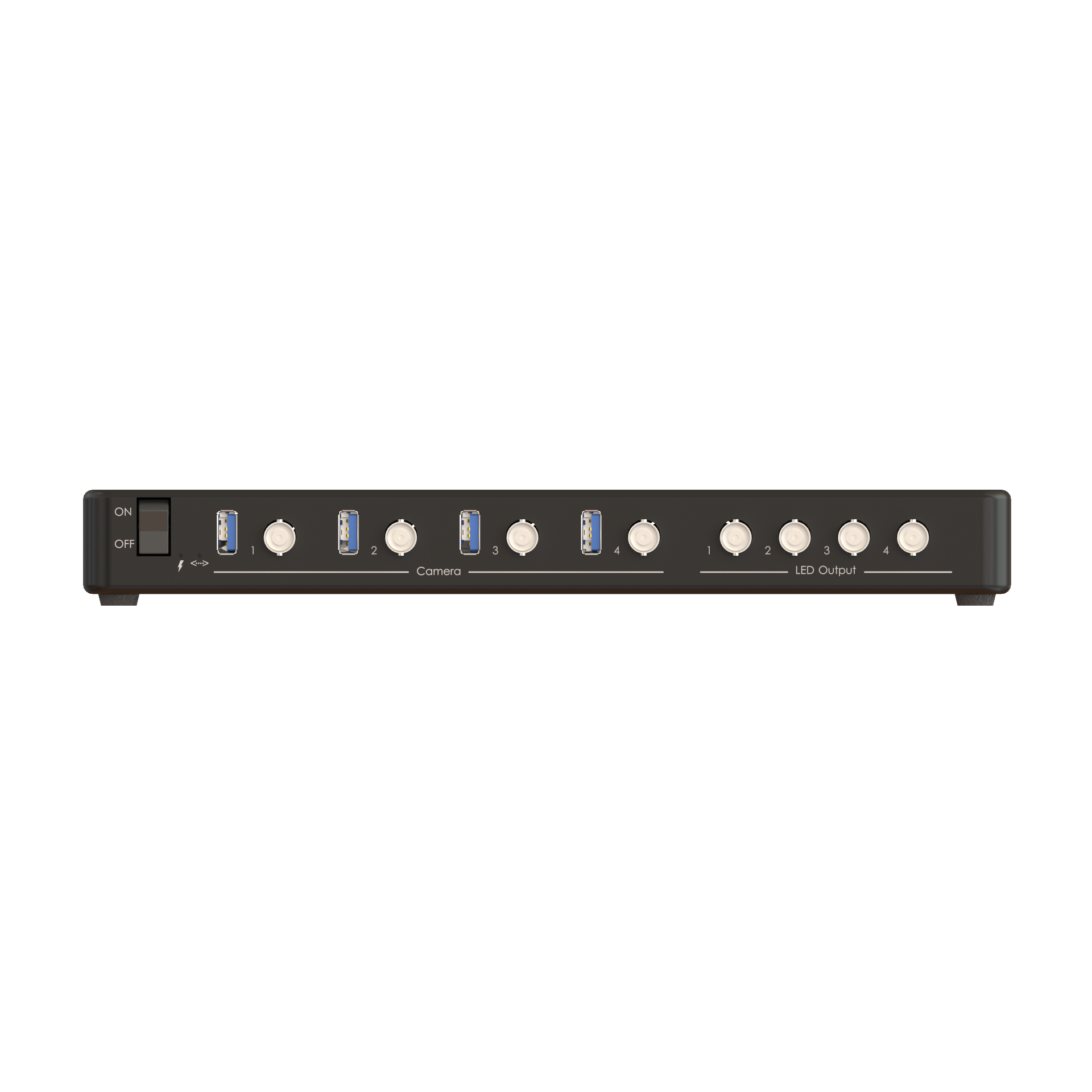
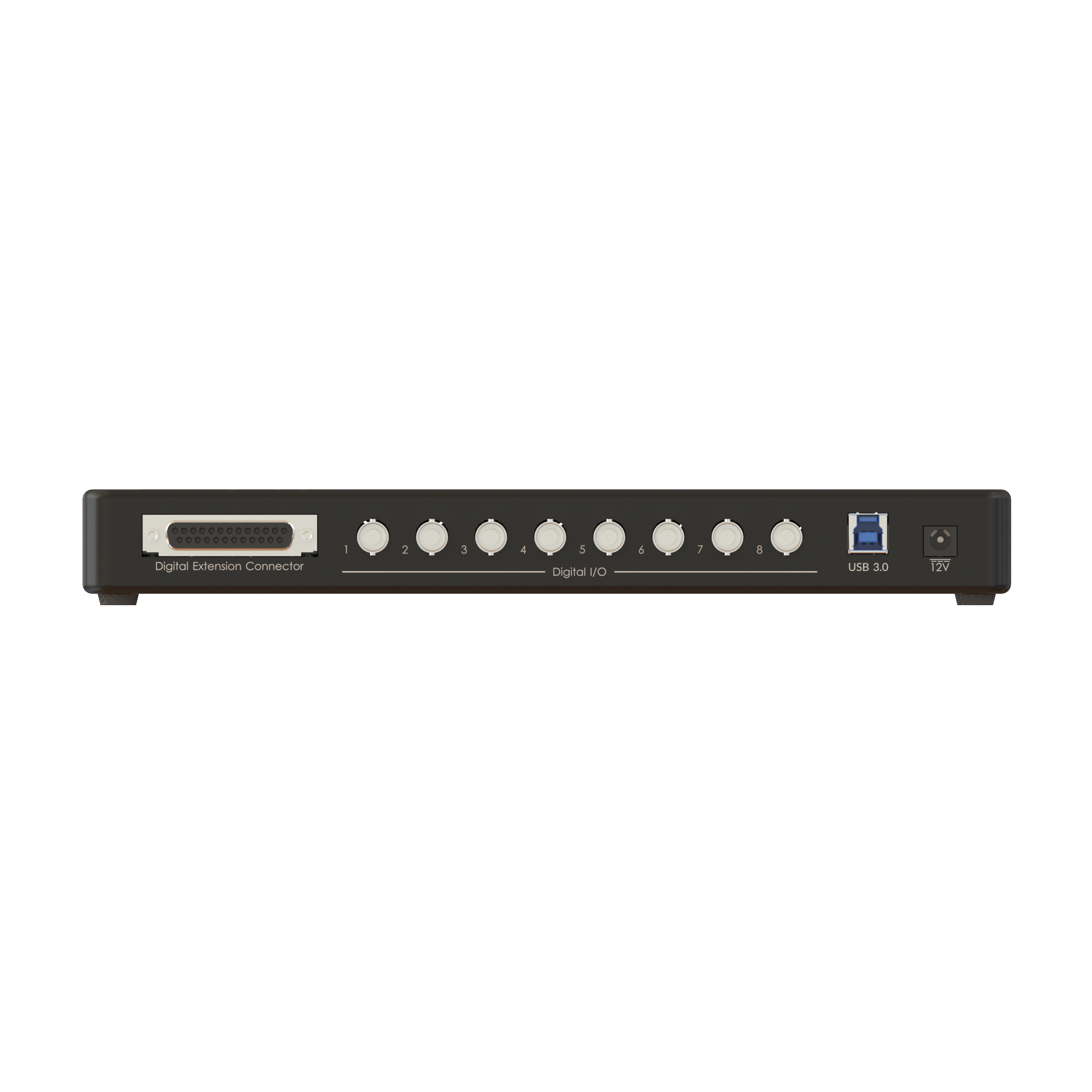
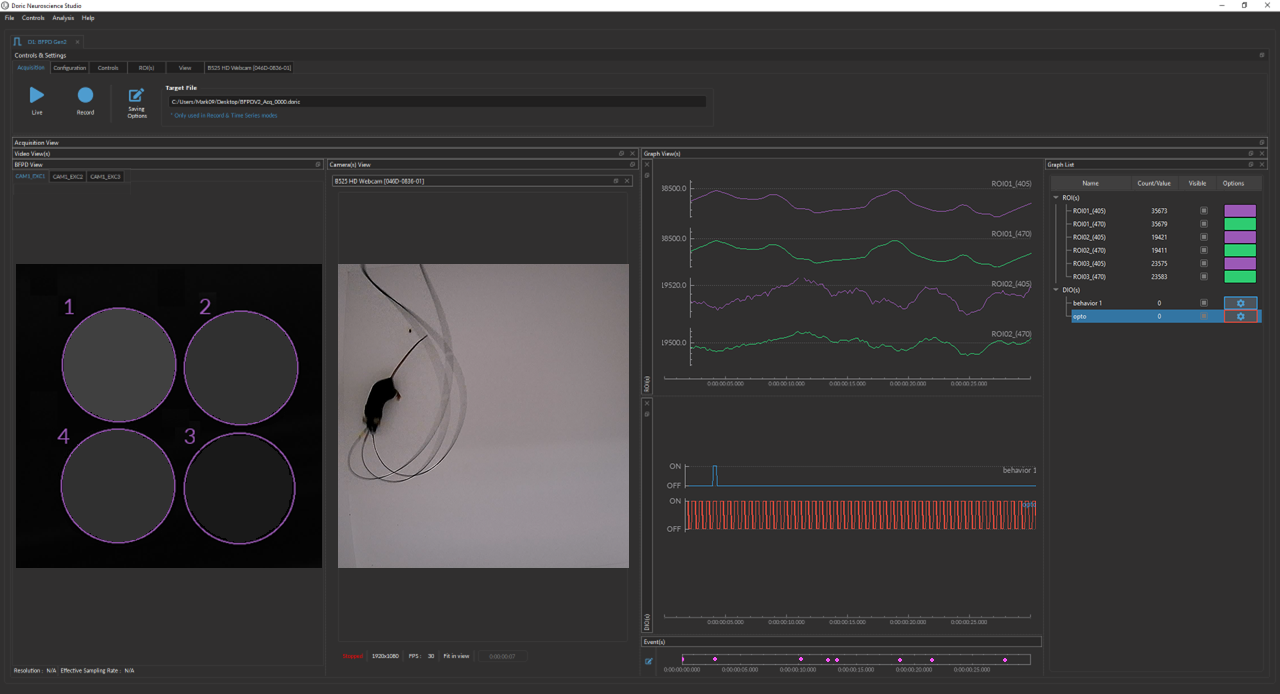
Optogenetics is often used to control neural activity during complex, freely-moving behavior to study the neural circuits underlying functions like decision making, memory formation, social interactions, sleep, etc. Doric provides several behavior solutions to record and synchronize videos and/or digital inputs/outputs for stimuli timing (tones, airpuffs, foot shocks, reward delivery, etc.) or behavior measures (lever presses, nose pokes, licks, etc.).
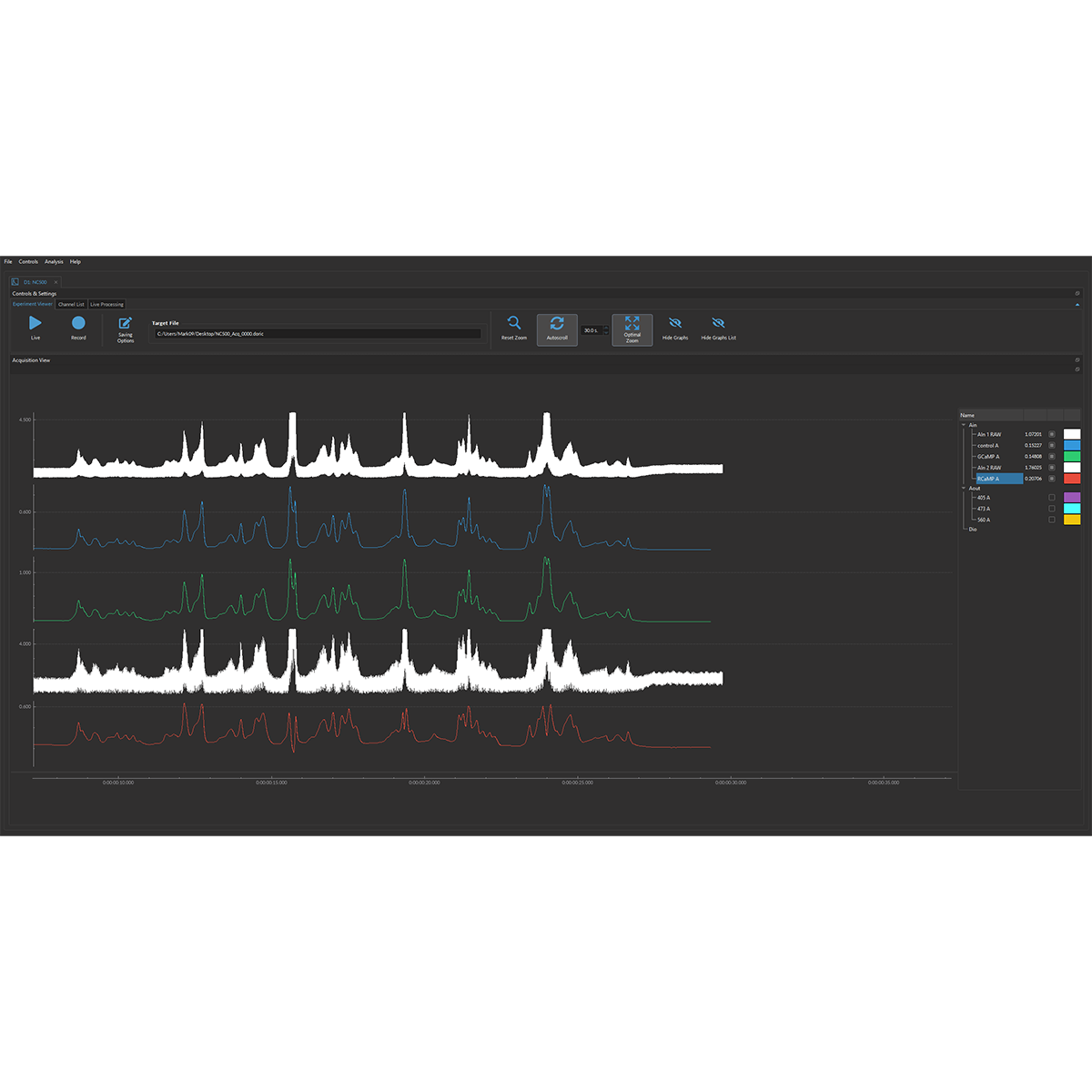
Fiber photometry can be combined with optogenetics at the same or different brain sites to simultaneously manipulate and record population-level neural activity. To avoid crosstalk with calcium indicators excited by blue light, only yellow or red wavelengths are used for optogenetic stimulation.
Different scenarios of combining photometry and optogenetics:
- Green indicators (e.g. GCaMP, dLight, etc.) photometry is compatible with optogenetics at the yellow-green range 580-680 nm filter)
- Green and red indicators (e.g. GCaMP and RCaMP) photometry is compatible only with red-shifted optogenetic (628-642 nm filter)
- Red indicators (e.g. RCaMP, jRGECO, etc.) photometry combination with blue light optogenetics, is not recommended, as commonly high intensity blue light causes artifacts in the red range, contaminating the photometry signal due to silica in the fiber optic patch cords.
All Doric photometry systems—including Basic, Rotary, Bundle, and FluoPulse lifetime photometry—are available in opto-compatible versions, with the exception of the wireless system.
👉 For more information, please visit the Photometry Solutions page or contact us at sales@doriclenses.com.
Optogenetics is often combined with fluid delivery in the brain using opto-fluidic cannula for simultaneous light stimulation and injection of drugs, viruses, neuromodulators or metabolites—enabling studies of neuromodulation, pharmacology, metabolism and circuit-specific behavioral effects such as anxiety, reward, and addiction.
The addition of opto-fluidic rotary joints provides simple solutions for drug injections during optogenetics experiments in freely-moving animals, making them ideal for combined opto-pharmacology or fluid infusion experiments.
👉 Learn more on the Optofluidics Solutions page.
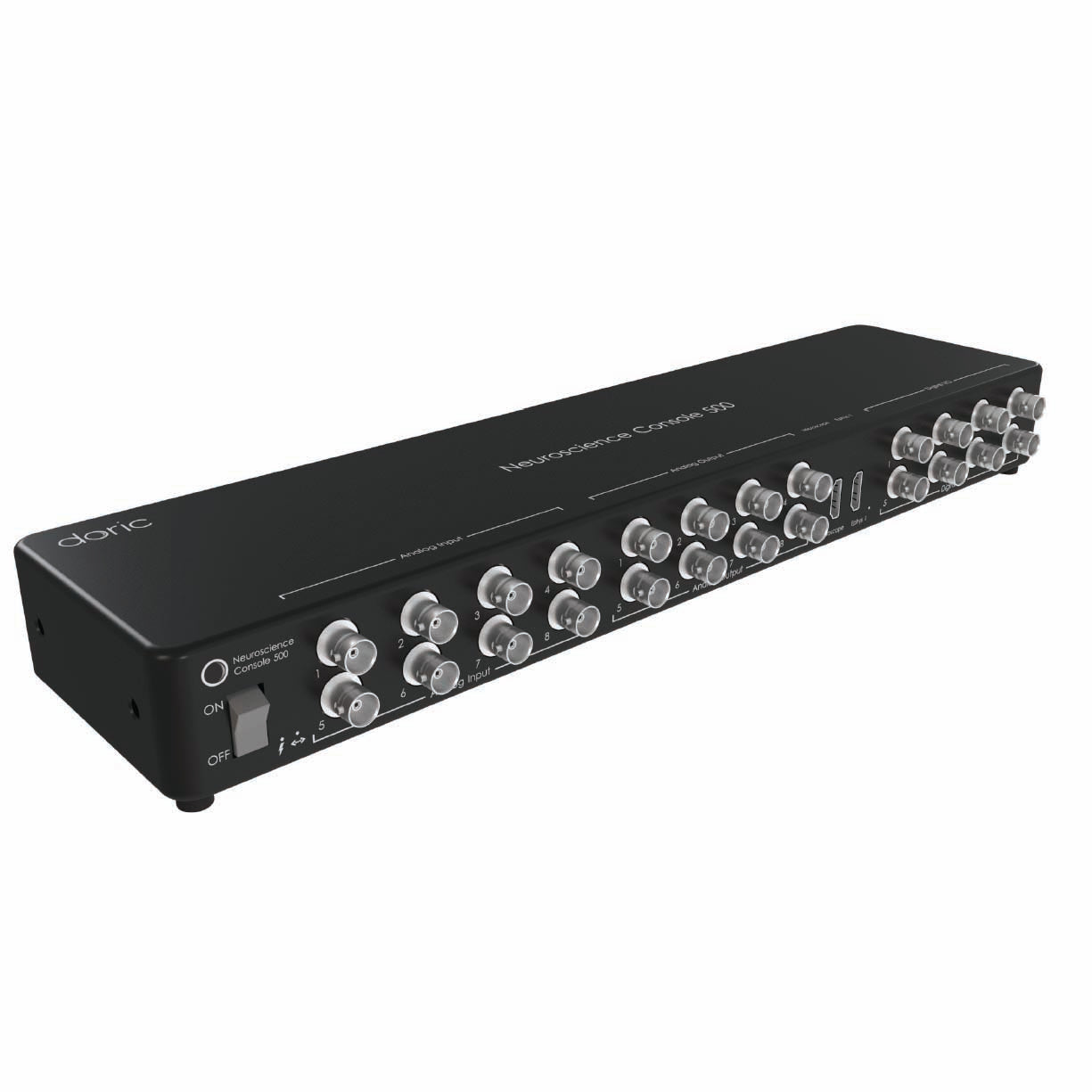
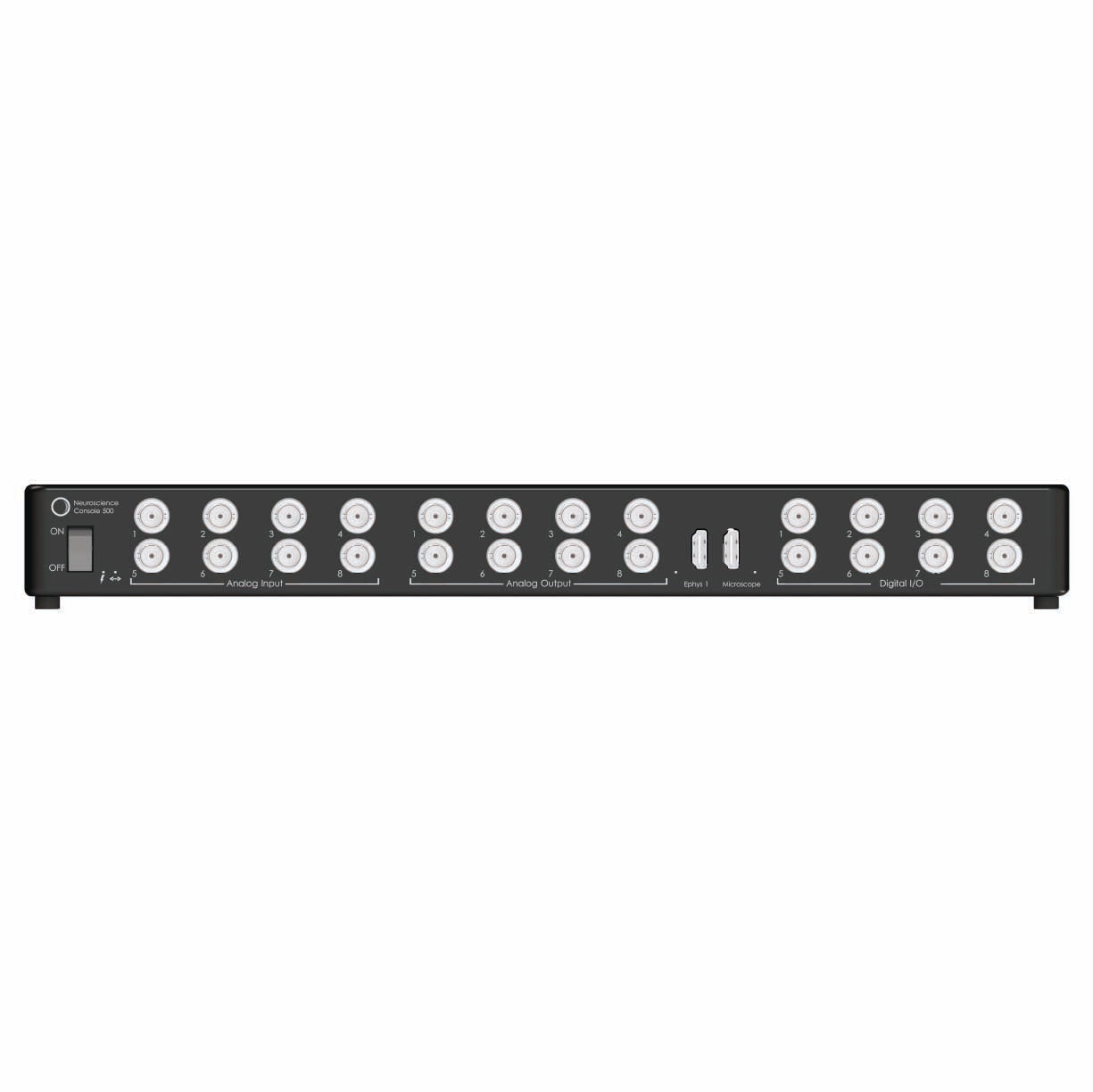
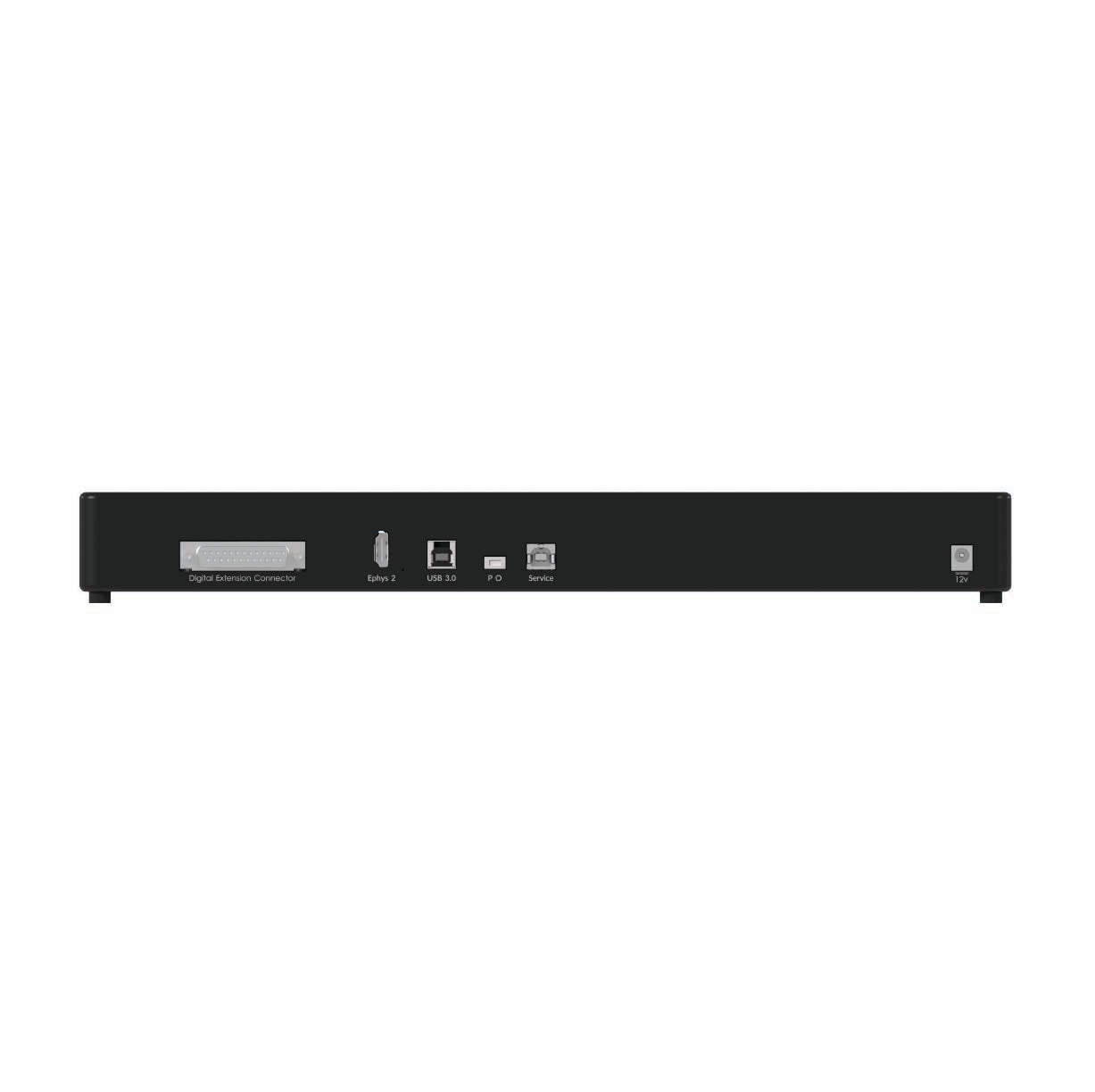
Optogenetics can be combined with various types of electrical recordings to study brain function with high temporal and spatial precision. This includes electrophysiology for single-unit, multi-unit, and local field potential (LFP) recordings, as well as opto-tagging to identify specific neuronal populations. In sleep studies, optogenetics is often paired with EEG/EMG to correlate neural activity with behavioral states.
Doric offers compatible tools such as data acquisition consoles (EPC, NC500), opto-electrical rotary joints, and opto-electric cannula to facilitate these integrated experiments.
👉 Learn more on the Opto-electrophysiology Solutions page.
Optogenetics can be combined with the Doric Miniscope to simultaneously manipulate and image single-cell neural activity in freely moving animals. Furthermore, the Doric miniscopes system compatible with optogenetics uses the LISER™ light source to deliver high-intensity (55 mW/mm2 at the tip of the implant) yellow-red light across a large field of view.
👉 Learn more on the Miniscope Solutions page.
User-friendly data acquisition software

Doric Neuroscience Studio
FREE data acquisition software
Intuitive software with multiple modalities for controling all doric devices, from minisope to photometry, behavior and optogenetics.
All-in-one data analysis software
danse™ - data analysis solution
Automate Find Cell with integrated CaImAn, MiniAn, or Suit2p and streamline your parameter selection with multiple preview steps, without any coding required!Align cell traces with animal behavior, for batch processing all in one software.