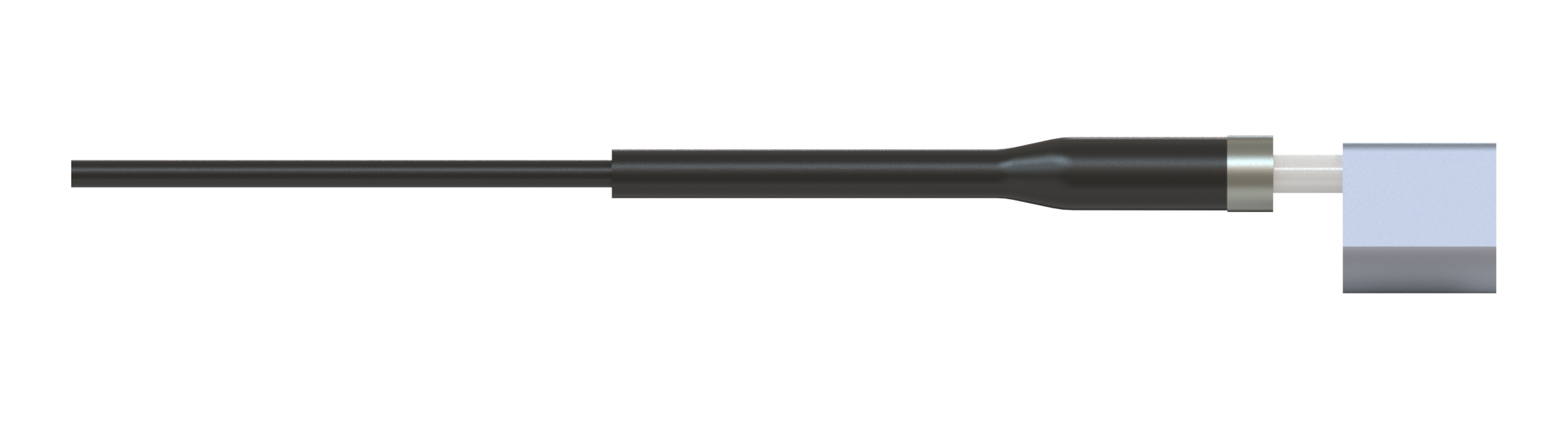
Mono Fiber-optic Patch Cords

-
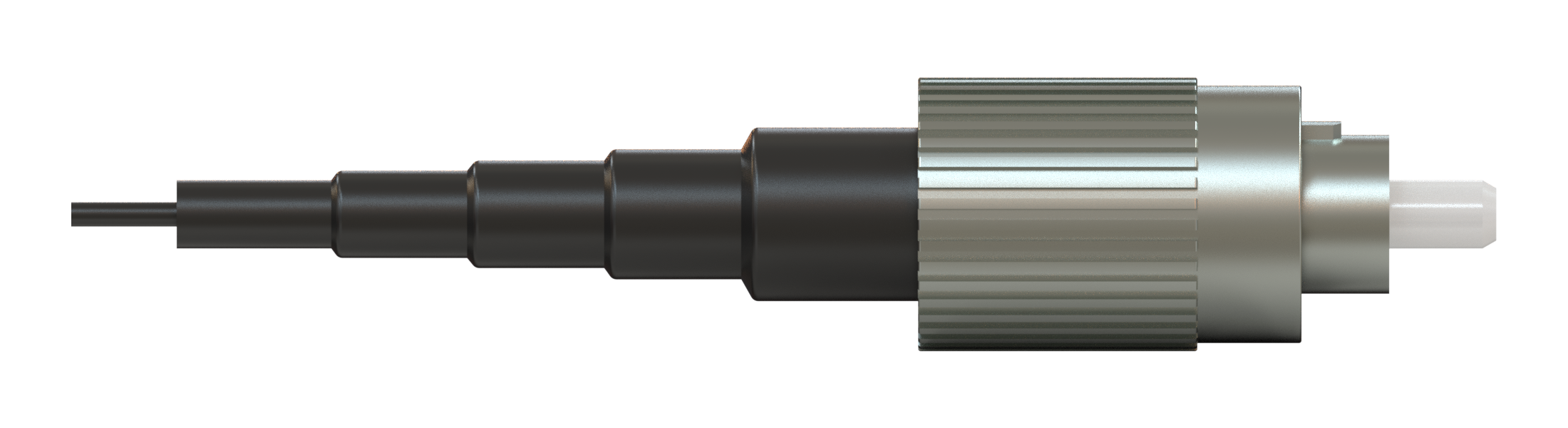
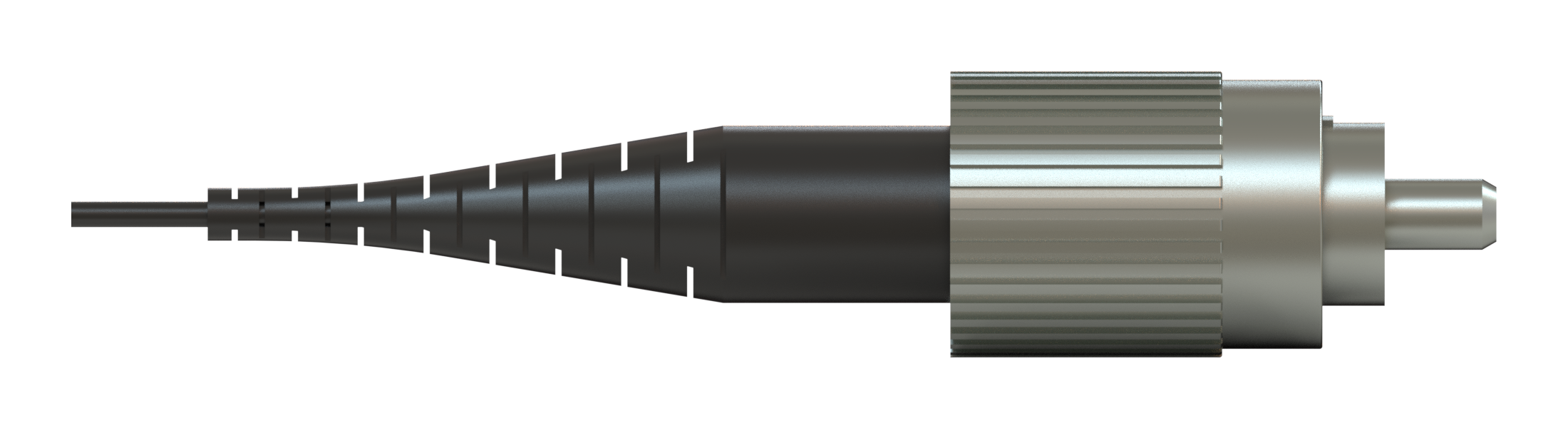
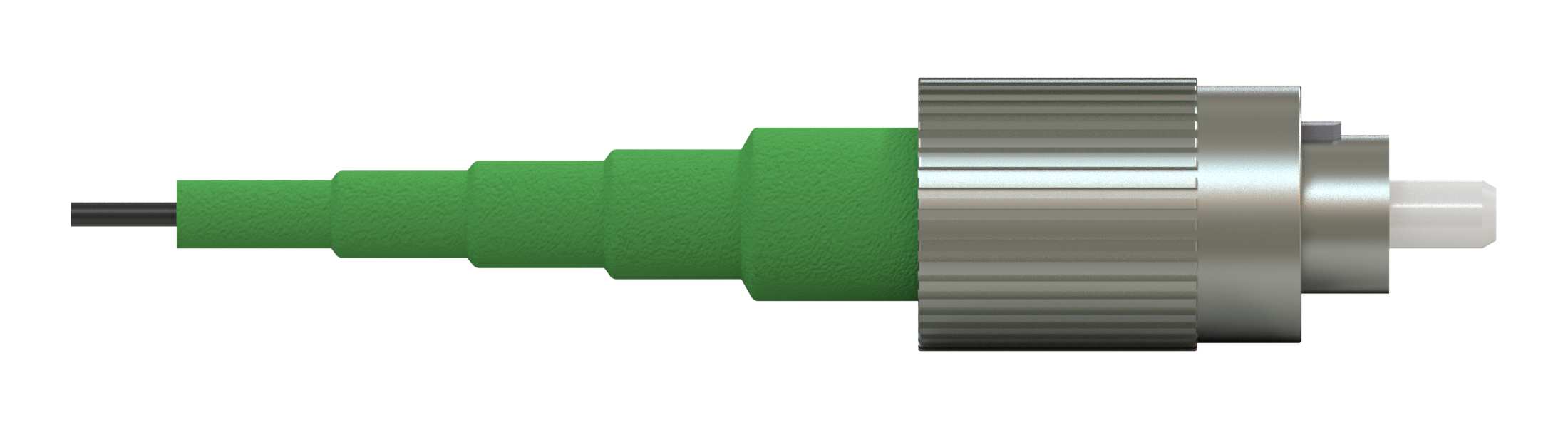
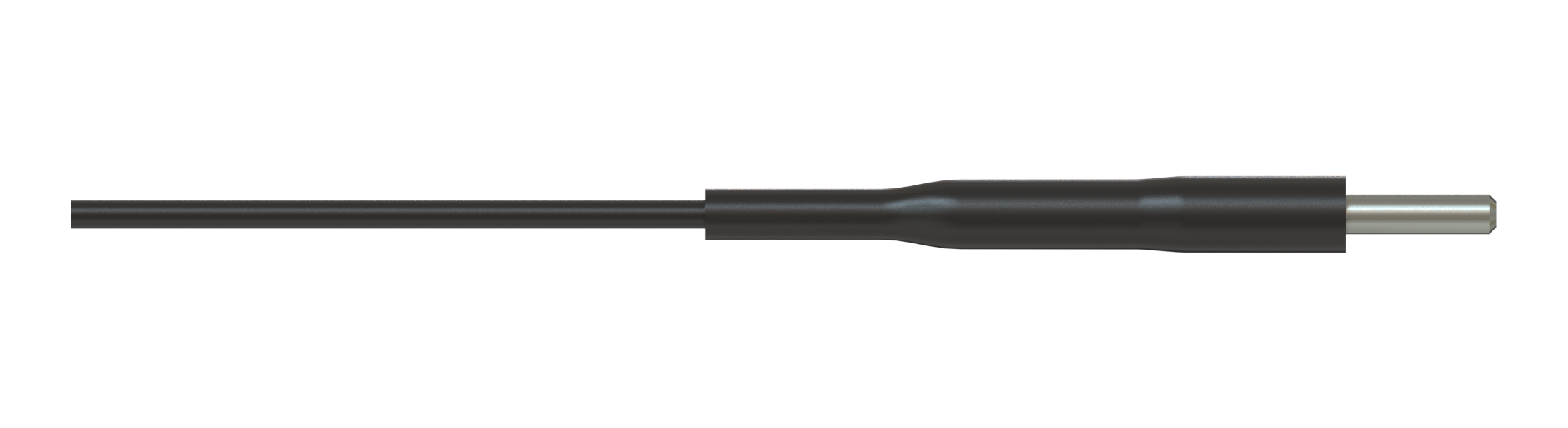
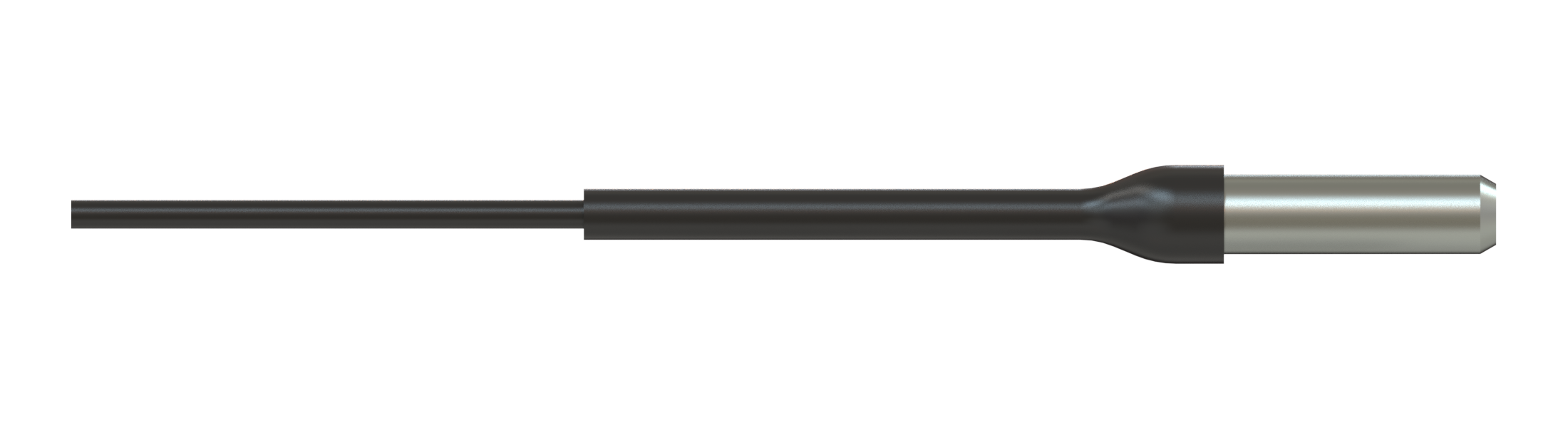
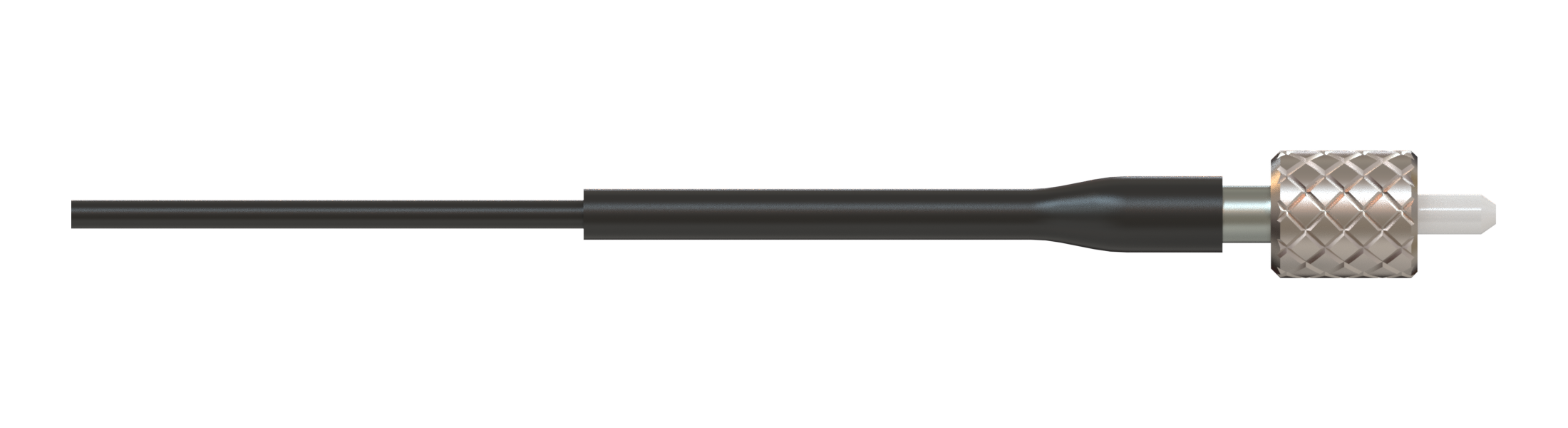
The simplest form of the fiber-optic patch cord is a single strand of optical fiber surrounded by a buffer and protective jacket with connectors at both ends.
The optical fiber core diameter and its numerical aperture (NA) define the coupling efficiency into the fiber.
The most popular optical fiber core diameters for optogenetics and fiber photometry experiments are those with 200 µm and 400 µm core diameters. As for the numerical aperture of the fiber, smaller 0.22 NA is suitable for laser light sources, while for incoherent light sources, like LEDs, it is recommended to use 0.5 NA and higher all the way from the light source to the sample.
Comparison Table : Patch cord Optical Fiber Type Optical Fiber Type Borosilicate Silica/Silica Silica/Polymer Plastic Core Glass Glass Glass Plastic Cladding Glass Glass Polymer Polymer Numerical Aperture 0.66 0.22 - 0.37 0.48 - 0.57 0.50 - 0.63 Flexibility Poor Good Good Excellent Auto-Fluorescence Good Excellent Good Poor RECOMMENDED USE : Fiber Photometry N/A
(too fragile)
Good* Good* Not recommended
(high AF)
Optogenetics LED Source N/A
(too fragile)
Not recommended
(low NA)
Good BEST Optogenetics Laser Source N/A
(too fragile)
BEST Good Good
* For Fiber photometry, we recommend low-autofluorescence optical fiber patch cords. -
Core/Cladding
MaterialCore
Diameter
(μm)Cladding
(μm)Buffer
(μm)NA Fiber-Optic Code* Silica/Silica 50 125 250 0.22 50/125/XXX-0.22 60 65 75 0.37 60/65/XXX-0.37 62.5 125 250 0.27 62.5/125/XXX-0.27 100 110 125 0.22 100/110/XXX-0.22 100 110 125 0.37 100/110/XXX-0.37 200 220 240 0.22 200/220/XXX-0.22 200 220 245 0.37 200/220/XXX-0.37 300 330 370 0.22 300/330/XXX-0.22 300 330 360 0.37 300/330/XXX-0.37 400 440 480 0.22 400/440/XXX-0.22 400 440 470 0.37 400/440/XXX-0.37 550 600 1040 0.22 550/600/XXX-0.22 600 660 710 0.22 600/660/XXX-0.22 600 660 710 0.37 600/660/XXX-0.37 Silica/Polymer 200 230 500 0.48 200/230/XXX-0.48 200 230 500 0.57 200/230/XXX-0.57 300 330 650 0.48 300/330/XXX-0.48 400 430 730 0.37 400/430/XXX-0.37 400 430 730 0.48 400/430/XXX-0.48 400 430 730 0.57 400/430/XXX-0.57 600 630 1040 0.48 600/630/XXX-0.48 Plastic/Plastic 240 250 - 0.50 240/250/XXX-0.50 240 250 - 0.63 240/250/XXX-0.63 480 500 - 0.50 480/500/XXX-0.50 480 500 - 0.63 480/500/XXX-0.63 735
750
- 0.50 735/750/XXX-0.50 735
750
- 0.63 735/750/XXX-0.63 960 1000 - 0.50 960/1000/XXX-0.50 960 1000 - 0.63 960/1000/XXX-0.63 1470 1500 - 0.50 1470/1500/XXX-0.50 1960 2000 - 0.50 1960/2000/XXX-0.50
* XXX is representative of the jacket code, see Jackets tab to choose the best one for your needs -
* Other color available on request.
Jacket availability may vary with optical fiber type -
- le choix d'une sélection entraîne une actualisation complète de la page








.png)
.png)

.png)

.png)
.png)

.png)

.png)

.png)
